Dental health is an integral part of overall health and can be related to several other ailments. Maintaining optimal dental health helps to mitigate such conditions. Besides this, maintaining oral hygiene helps build confidence and self-esteem and can help you in social situations.
Cavities are one such dental ailment that can leave you feeling conscious while affecting your health. You are at greater risk for cavities if you don't maintain oral hygiene. If you have a cavity, you must get a root canal done or remove the complete tooth.
You might also be affected by gingivitis, which can be incredibly painful and make you avoid food.
What is a cavity?
A cavity is a hole in your tooth. Cavities are caused due to various reasons, such as frequently munching on snacks, drinking sugary beverages, and not cleaning your teeth, including bacteria in your mouth.
Cavities are among the most common oral health problems. If cavities are not treated on time, they get large and can get deep into the layer of your teeth causing extreme tooth pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
Regular brushing, flossing, and visiting your dentist at least every six months help you keep cavities at bay.
Even if you have cavities, you will not realize until you notice other symptoms. Cavities can cause permanent damage to your teeth that can not be cured. You need to get a root canal or get your tooth removed by a dentist.
What causes cavities?
Cavities are caused by growing tooth decay that occurs in three stages. They are,
i). Plaque build-up
If you eat a lot of sugar, including starches, and don't clean your teeth efficiently, plaque will build up due to bacteria catering to those sugars. Plaque is a transparent film that is slightly sticky. You may notice it when you have not brushed your teeth for longer.
If plaque is not removed, it hardens and turns into tough tartar that is difficult to remove by brushing your teeth. A plaque can also form below the gum line and cause severe gum diseases or periodontitis.
ii). Plaque attack
Plaque erodes all the minerals in the enamel on the surface of the teeth, causing tiny openings. These small openings are the beginning stage of the cavities, encouraging the acids and bacteria in the plaque to move toward the dentin. Dentin consists of microscopic tubes that protect the nerves. This leads to tooth sensitivity which is the calling card of cavity formation.
iii). Continual tooth destruction
Without intervention, tooth erosion gets deep into the innermost tooth material, the pulp. Bacteria can cause inflammation and swelling in the pulp, causing severe pain in the nerve. The pain can also extend to above and below the tooth.
Other causes of cavities include:
iv). Saliva:
Saliva acts as an invisible agent in protecting teeth from various oral health problems. Salivary diseases can affect your ability to chew, speak, eat, and swallow. However, saliva plays an essential role in cavity development. Saliva washes away harmful bacteria and protects your teeth from getting cavities.
v). Acid:
When stomach acid moves into the mouth, it can easily affect the tooth enamel, also known as tooth erosion. Without the protective layer of tooth enamel, the teeth are at high risk of tooth decay, sensitivity, and discoloration of teeth.
vi). Left-over food:
Even the tiniest food stuck in your teeth can cause a risk for a healthy tooth. Food stuck is not the problem, but what happens to it is. The mouth is full of bacteria; some are beneficial, while others are harmful. As the bacteria eat the leftover solid food, acids become bi-products and damage the teeth' enamel.
Symptoms of Cavity
Symptoms of a cavity may include,
- Toothache: Continues pain that seemingly occurs without any reason.
- Sensitivity: You may notice one of your teeth is more sensitive to changes in temperature than usual when you eat or drink something cold or hot, you may experience sensitivity in that particular tooth.
- Discoloration: You might see white or brownish spots on your teeth, and it's a sign of underlying dental health problems.
- Hole in the tooth: You may notice a small hole or large opening or a crack in the tooth that warns of a cavity.
- Bad breath: Bad breath could just result from some food you eat, such as onions. Bad breath that doesn’t go away can be a sign of cavities. Persistent bad breath is a sign of gum disease.
- Swelling and bleeding gums: You may observe your gum look raw, red, or swollen, incredibly close to the tooth line. There might be some bleeding gum as well.
What does a cavity look like?
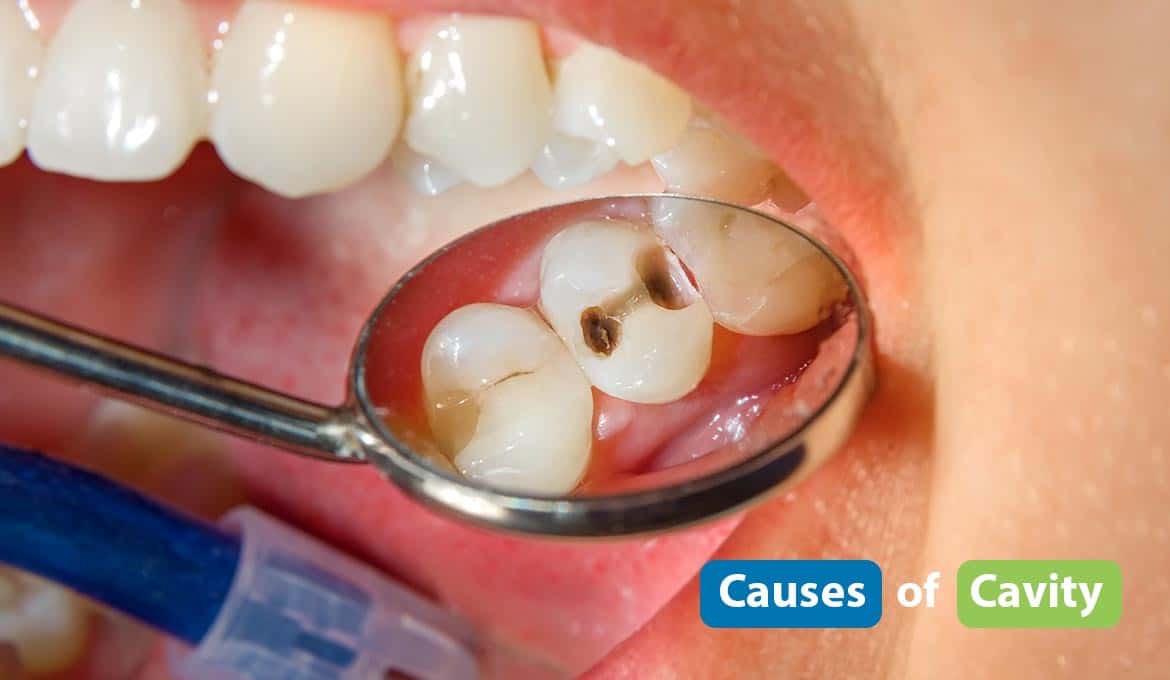
Cavities often look like dark spots on your tooth—generally brown, yellow, or black. The cavity might look like a stain or slight discoloration in the early stage. Gradually the hole gets bigger and darker. A tiny hole can potentially eat the entire tooth.
Cavities come in all different sizes and shapes. The size of the cavity depends on how far the cavity has been present and how much damage it has caused.
How to prevent cavities?
Prevention sometimes works best in the case of cavities. You can avoid the loss of minerals in your teeth and restore those minerals, so you won’t be at risk of losing your tooth or developing cavities in the future. This is a process known as remineralization. Brushing your teeth twice a day is one of the best ways to prevent cavities.
Use toothpaste with fluoride content, and you can brush away any of the leftovers and bacteria that build up plaque on your teeth and at your gum line. When you brush your teeth with fluoridated toothpaste, you’re also helping the enamel on your teeth repair and remineralize.
Studies have shown that high-fluoride toothpaste is more effective than toothpaste without fluoride.
Following are some of the steps you can consider to maintain your oral health. They include,
- Brush your teeth twice a day: Brushing your teeth twice daily (Morning and night after dinner) can reduce plaque formation and help you keep your oral health intact.
- Floss once a day: Flossing once daily is another way to avoid plaque buildup on your teeth. Hold the dental floss tight between your thumb and index fingers, and slide it up and down between your teeth gently.
- Swish with water: After food, if the food is stuck in your tooth, drink water and swish as water will wash away the leftover food that might lead to plaque formation.
- Oil pulling: You can practice oil pulling to keep your teeth healthy. Oil pulling reduces the risk of inflammation, bad breath, and cavities. For this, take a tablespoon of coconut oil or olive oil and swish it around for about 20 minutes in the morning on an empty stomach.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash that kills bacteria and washes away any bacteria between your teeth.
- Visit the dentist: Regularly visit your dentist to check and track your oral health.
- Avoid eating hot or cold: Avoid eating any food item that is extremely cold or hot if you have teeth sensitivity that causes tooth decay.
- Avoid consuming sugary food and beverages: Avoid sugary drinks and food. Too much intake of sugary food items can damage your teeth and cause cavities.
- Don't use your teeth as tools: Don’t unlock bottles and tins using your teeth, as they can harm your teeth.
- Avoid tobacco products: Avoid smoking, pan masala, and other tobacco products. These products not only harm your oral health but also cause some severe health conditions like cancer.
- Drink plenty of water: Drink plenty of water, especially after you eat something. Drinking lots of water washes away any leftover food stuck between your teeth and can cause plaque buildup.
Risk factor of cavities
Various factors might put you at risk for cavities. They are:
- Consuming sugary foods like milk, sweets, soda, and dried fruit that cling to the teeth and are not easily washed by saliva.
- Drinking soda or sugary drinks (beverages) daily.
- Eating junk foods.
- Low levels of saliva in the mouth
- Inadequate fluoride
- Age
- Infrequent brushing
- Eating disorders – can also potentially cause tooth erosion from repeated vomiting or lack of saliva production.
When to consult your dentist?
Generally, you should visit your dentist for regular dental at least every six months. This can differ based on your needs and your teeth. The American Dental Association recommends scheduling regular appointments with a dentist for routine dental examinations.
You shouldn’t wait until your next appointment if you feel any abnormality or pain in your teeth.
Visit your dentist anytime you observe any change in your gums or teeth, mainly if there’s pain or swelling. So, if your gums are puffy and bleeding or one of your teeth begins aching, you should see your dentist.
Conclusion
See your dentist for routine checkups, especially if you experience pain or swelling. If a dentist notices any cavity or tooth decay on one of your teeth, they’ll talk with you and discuss the best way to treat the condition, typically a filling.
In severe conditions, your dentist may advise removing the complete tooth to avoid the cavity spreading to other teeth.
It is advisable to follow proper dental hygiene to prevent such dental ailments from ever occurring altogether.
FAQs
1. What is a cavity?
Ans. Cavity refers to holes formed in the teeth due to dental issues like plaque which bacteria and poor dental hygiene can aggravate.
2. How to prevent cavities?
Ans. Cavities can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing once, and visiting a dentist every six months, can help you prevent dental health issues from arising.
3. Can cavities result in tooth loss?
Ans. Cavities start as a mild incision on your outer tooth that can progressively worsen enough to penetrate your inner tooth pulp. If the cavity has developed to such an extent and leads to inflammation caused due to bacteria, then cavities can lead to tooth loss.
4. Are sensitive teeth a sign of a cavity?
Ans. Teeth sensitivity is caused when the nerves in the gum feel the brunt of actions on the outer enamel of the teeth. This can happen due to incisions in the channels connecting the enamel to the inner nerves. This can be an early indication of cavities, and quick action is required to mitigate further inroads from your cavities.
5. What are the risk factors for cavities?
Ans. Several factors, like poor dental hygiene, age, lifestyle choices, consumption of a sugary diet, proper brushing habits, etc, can contribute to a higher chance of developing cavities. Brushing properly twice a day, flossing once, and visiting a dentist 1-2 times a year can help you avoid dental ailments like cavities.
Read Also: